The Science of Yoga (Part 1 of 3): Introduction
Have you ever wondered why yoga and meditation make you feel so good? Modern neuroscience research reveals just what is happening in our brains when engaging in yoga and mindfulness practices.
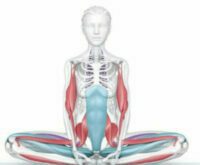
Did you know that yoga can lower your blood pressure, decrease inflammation, and prevent age-related atrophy of the brain? Yoga affects more than just your muscles and bones; it positively impacts every system of your body. Yoga builds muscle strength and improves flexibility, agility, and balance. It helps to handle challenges with grace. Practicing yoga philosophy can also help you find purpose and meaning in your life.
What is the Origin of Yoga?
The ancient art of yoga has been around for over 5,000-years. The origin of the word ‘Yoga’ is from the Sanskrit root ‘Yuj,’ meaning ‘to join’ or ‘to yoke’ or ‘to unite.’ As per Yogic scriptures, the practice of Yoga leads to the union of individual consciousness with that of ‘Universal Consciousness,’ indicating a perfect harmony between the mind and the body.

Yoga Today
Studies are also increasingly documenting how yoga works. Advances in technology are revealing that the healing power of yoga can transform the entire body. Yoga research has expanded exponentially in the last 20 years thanks to funding from The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), a division of the National Institute for Health (NIH). These studies (“Yoga: Effectiveness and Safety“) have documented yoga’s efficacy for:

“Yoga doesn’t just affect your muscles and bones; it affects every single system of your body. Yoga is a complete way of considering the world and being in it. The practice of this ‘lifestyle technology’ includes poses known as asanas and breathwork known as pranayama, meditation and philosophical teachings. ” —Ann Swanson, author of Science of Yoga: Understand the Anatomy and Physiology to Perfect Your Practice
For more information, see
How Yoga Can Enhance Your Brain (Part 2 of 3) and The Health Benefits of Yoga (Part 3 of 3).