The Science of Yoga (Part 2 of 3)
“Scientists predict that we only observe and understand 4% of the universe in which we live. Similarly, we are only on the frontiers of exploration when it comes to the science of the human brain, mind, and consciousness, which gets to the heart of yoga capacity for transformation.” —Ann Swanson, author of Science of Yoga: Understand the Anatomy and Physiology to Perfect Your Practice
Groundbreaking neuroscience research is being conducted on mindfulness, meditation, and yoga. The results of this research have been quite profound in terms of the mechanism of exactly what’s happening in our neurobiology when we meditate, chant, or do different intentional breathing exercises.
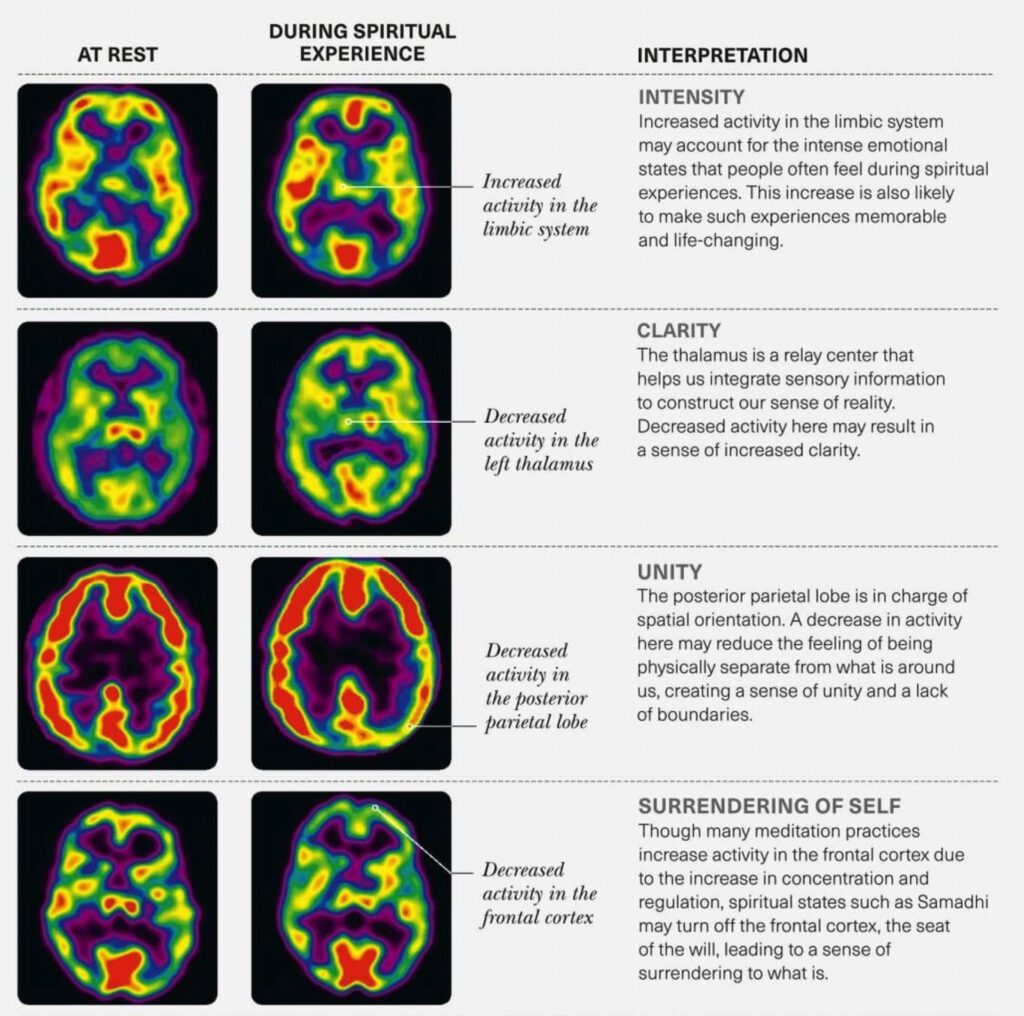
Andrew Newberg, M.D., applies the scientific method to spirituality through brain imaging studies. Newberg developed a study where he scanned the brains of meditating and chanting Buddhists, Sikhs, and praying nuns undergoing mystical experiences. They reported feelings of timelessness, spacelessness, and transcendence. Newberg compared his subjects’ brain scans at rest and then their scans while having transcendental spiritual experiences. This comparison helped him to identify specific brain activity patterns associated with spirituality.
Dr. Andrew Newberg’s groundbreaking work has been covered in several companion Beawake articles:
Four Common Brain Patterns in Spiritual Experiences
Yoga Builds New Neural Pathways
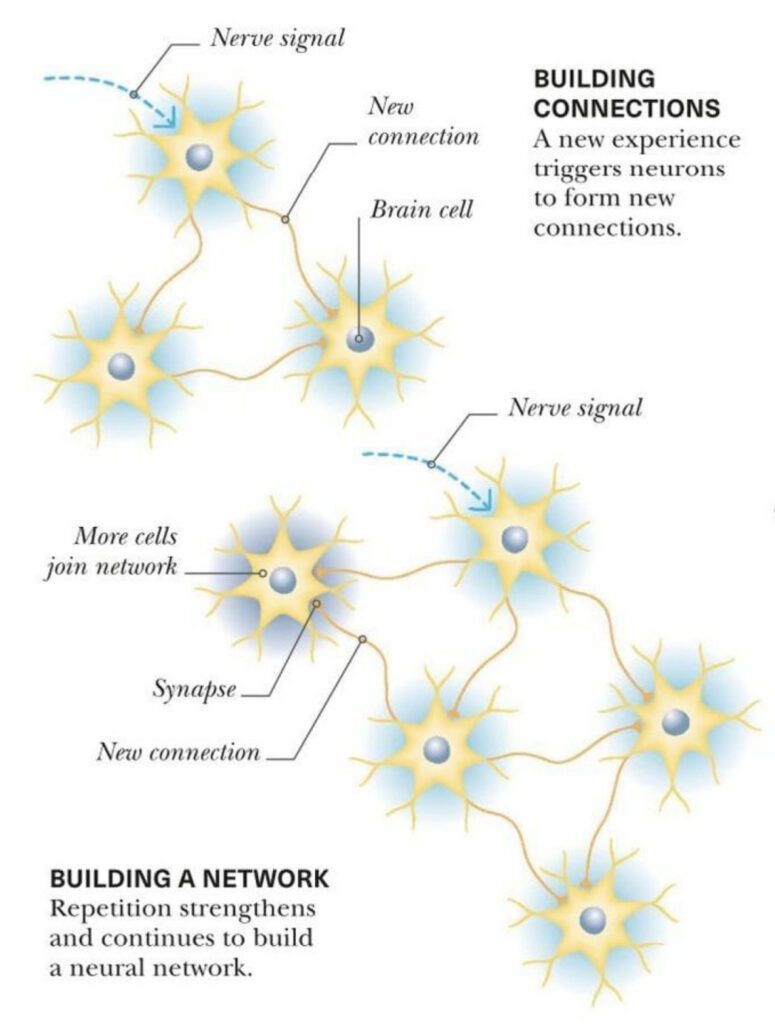
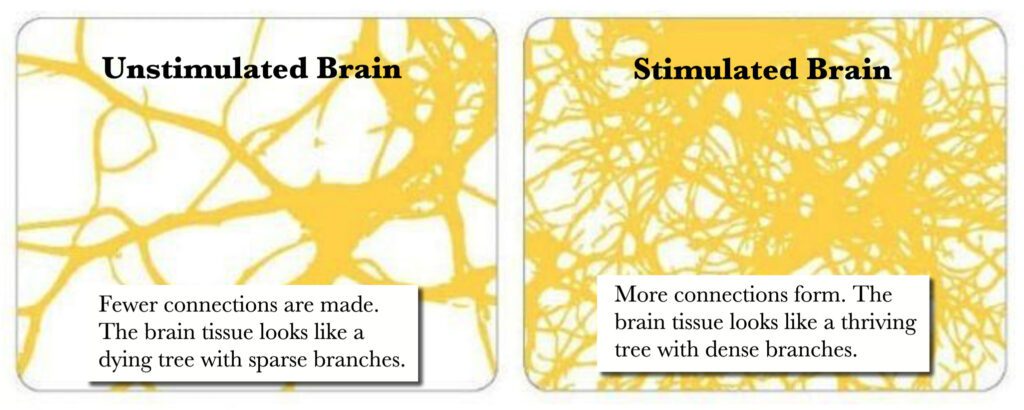
Yoga can help the brain develop and strengthen new neural connections and neural pathways. Your brain eventually becomes conditioned based on your choices and experiences.

Yoga can help the brain develop and strengthen new neural connections and neural pathways. The more you practice an activity or a mindset, the more neural connections are created. Your brain eventually becomes conditioned based on your choices and experiences. With approximately 100 billion neurons, the brain’s possible connections are vast. Yoga can help grow these neural pathways.
Neuroplasticity - Your Brain Can Grow
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a protein responsible for neuroplasticity. Recent cutting-edge discoveries reveal that our brains are similar to flexible plastic that is continuously being reshaped by our experiences. This flexibility is called neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to form and remap synaptic connections, especially in response to learning and engaging in both the mind and body, such as yoga.
“Scientists have shown that thinking, learning, and acting can turn our genes on or off, thus shaping our brain anatomy and our behavior — surely one of the most extraordinary discoveries of the twentieth century.” Norman Doidge, M.D., bestselling author of The Brain That Changes Itself: Stories of Personal Triumph from the Frontiers of Brain Science
Not long ago, scientists thought the brain could not grow after childhood and started degrading after the age of 25. Now we know that nerve tissue in the brain adapts and can indeed grow after childhood. Your brain tissue either develops or atrophies based on the level of stimulation. Yoga improves neuroplasticity, which helps with memory issues, brain fog, concentration, anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline.
How Yoga Affects the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is where emotions are processed, creating blissful feelings, also known as “the yoga high.” Scientists wanted to validate whether this feeling was just a figment of imagination or yoga causing real physical responses. Numerous recent studies reveal that these effects are indeed real. This yoga high is not just a fleeting feeling. In actuality, it indicates some genuine physical responses that lead to sustained feelings of reduced stress and improved mood and health.
During yoga, you are lengthening and strengthening your muscles while also taking deep breaths. Deep breathing and stretching oxygenate your blood, which in turn activates your parasympathetic nervous system. The parasympathetic nervous system decreases heart rate and blood pressure and increases digestion, thus influencing your brain’s limbic system. To activate the parasympathetic nervous system, you need to do poses that encourage deep relaxation. The best yoga poses for this are forward bends, hip openers, sitting, and lying down while facing up poses.
For more information, see The Science of Yoga (Part 1 of 3) and The Health Benefits of Yoga (Part 3 of 3).